Lung Diseases
Lung diseases are some of the most common medical conditions in the world. Tens of billions of people have lung disease in the world. Smoking, infections, and genes cause most lung diseases. Your lungs are part of a complex system, expanding and relaxing thousands of times each day to bring in oxygen and send out carbon dioxide. Lung disease can happen when there are problems in any part of this system. There are three main types of lung disease:
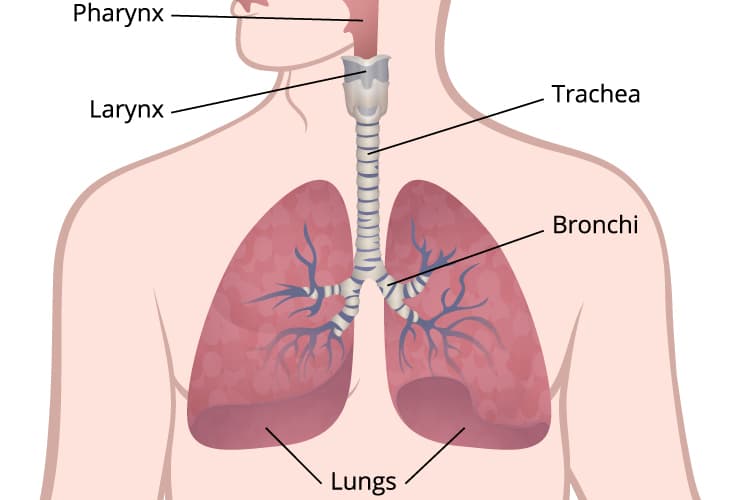
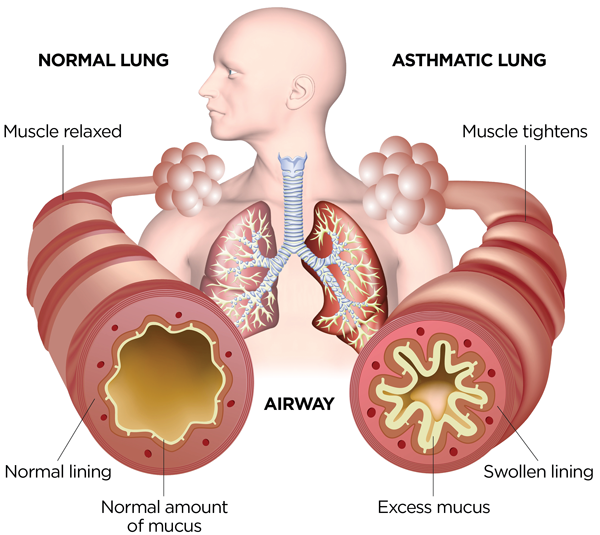
Airway Diseases
These diseases affect the tubes (airways) that carry oxygen and other gases into and out of the lungs. They usually cause a narrowing or blockage of the airways. Airway diseases include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and bronchiectasis. People with airway diseases often say they feel as if they’re “trying to breathe out through a straw.”
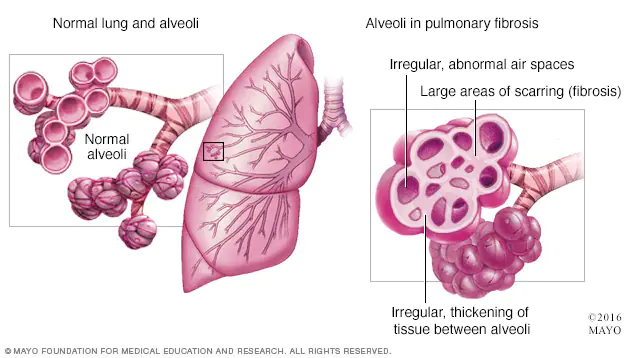
Lung Tissue Diseases
These diseases affect the structure of the lung tissue. Scarring or inflammation of the tissue makes the lungs unable to expand fully (restrictive lung disease). This makes it hard for the lungs to take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide. People with this type of lung disorder often say they feel as if they are “wearing a too-tight sweater or vest.” As a result, they can’t breathe deeply. Pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis are examples of lung tissue disease.
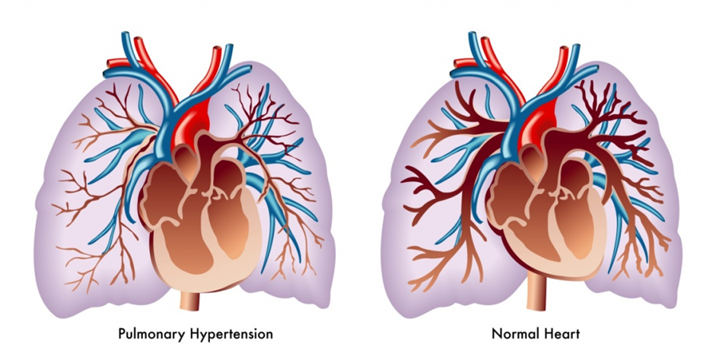
Lung Circulation Diseases
These diseases affect the blood vessels in the lungs. They are caused by clotting, scarring or inflammation of the blood vessels. They affect the ability of the lungs to take up oxygen and release carbon dioxide. These diseases may also affect heart function. An example of a lung circulation disease is pulmonary hypertension. People with these conditions often feel very short of breath when they exert themselves.
Many lung diseases involve a combination of these three types. The most common lung diseases include:
- Lung cancer
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Asthma
- Collapse of part or all of the lung (pneumothorax or atelectasis)
- Swelling and inflammation in the main passages (bronchial tubes) that carry air to the lungs (bronchitis)
- Lung infection (pneumonia)
- Abnormal buildup of fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema)
- Blocked lung artery (pulmonary embolus)
Here we will discuss first three which are most common of all.
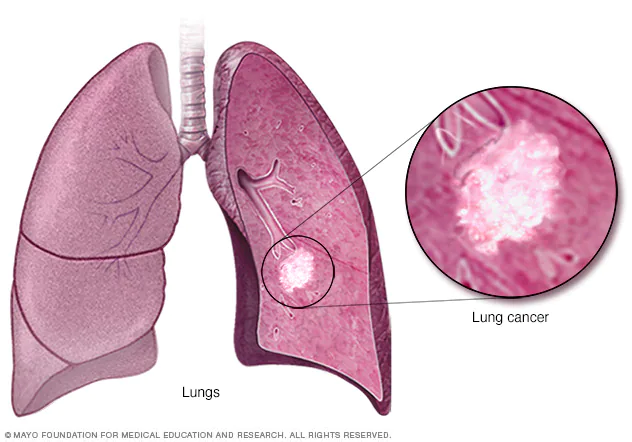
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the lungs. Your lungs are two spongy organs in your chest that take in oxygen when you inhale and release carbon dioxide when you exhale. Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide.
People who smoke have the greatest risk of lung cancer, though lung cancer can also occur in people who have never smoked. The risk of lung cancer increases with the length of time and number of cigarettes you’ve smoked. If you quit smoking, even after smoking for many years, you can significantly reduce your chances of developing lung cancer.
Deaths by lung cancer (approx. 90% due to smoking tobacco) and greater than deaths by colon cancer, breast cancer and pancreas cancer combined.
Characteristics of Lung Cancer
- Men who smoke have 23 times chances of lung cancer than non smoker men
- Women who smoke have 13 times chances of lung cancer than non smoker
- Non smokers have 20-30% higher risk of developing lung cancer if they are regularly exposed to cigarette smoke
How Quitting smoking benefits health and how fast ?
- Just after 20 mins of quitting, heart rate and blood pressure drops.
- Within few weeks, your blood circulation and lung function improve.
- Within few months, the sweeper cells that help clean the lungs, remove mucus, and reduce the risk of infection start to grow.
- Within a year of quitting, your smoking related risk of coronary heart disease becomes half that of current smokers.

Toxic Effects of Cigrattes on lungs
Tobacco smoke contains chemicals that weaken the body’s immune system, making it more susceptible to disease and handicapping its abilities to destroy cancer cells. At the same time, tobacco smoke can damage cell DNA, increasing the chance for cancer cells to form and flourish in the first place.
Benefits of Broccoli and Turmeric
Broccoli boost the activity of the detoxifying enzymes in the liver, which help to clear carcinogens before they even made it to smoke cells. Such vegetables as broccoli, cabbage and cauliflower help prevent damage to lungs.
Turmeric may help prevent some of the DNA damage caused by smoking. This is because of curcumin (bright yellow pigment in turmeric).

Curcumin as Cancer Preventing Agent
Chemopreventive (cancer-preventing) agents can be classified into different subgroups based on which stage of cancer development they help to fight : – Carcinogen blockers and antioxidants help prevent the initial triggering DNA mutation and antiproliferatives work by keeping tumors from growing and spreading. Curcumin is special in that it appears to belong to all three groups, meaning it may potentially help prevent and/or arrest cancer. The anticancer effects of curcumin extend beyond its ability to potentially prevent DNA mutations. It also appears to help regulate programmed cell death. Your cells are pre-programmed to die naturally to make way for fresh cells through a process known as apoptosis. It means, your body is rebuilding itself every few months with the building materials you provide it though your diet. Some cells, however, overstay their welcome- namely, cancer cells. By some how disabling their own suicide mechanism, they don’t die when they’re supposed to. Because they continue to thrive and divide, cancer cells can eventually form tumors and potentially spread throughout the body. Curcumin has the ability to reprogram the self-destruct mechanism back into cancer cells.
Dietary Second hand smoke
Another contributing cause of lung cancer may be carcinogenic plume : fumes from frying. When fat is heated to frying temperatures, whether it be animal fat, such as lard, or plant fat, such as vegetable oil, toxic volatile chemicals with mutagenic properties (those able to cause genetic mutations) are released into the air. If you do fry at home, good ventilation in the kitchen may reduce lung cancer risk. Living next to a restaurant may pose a health hazard. Although all meat may release potentially carcinogenic fumes, processed meat like bacon may be the worst . Bacon fumes cause about four times more DNA mutations than the fumes from beef burgers fried at same temperatures.

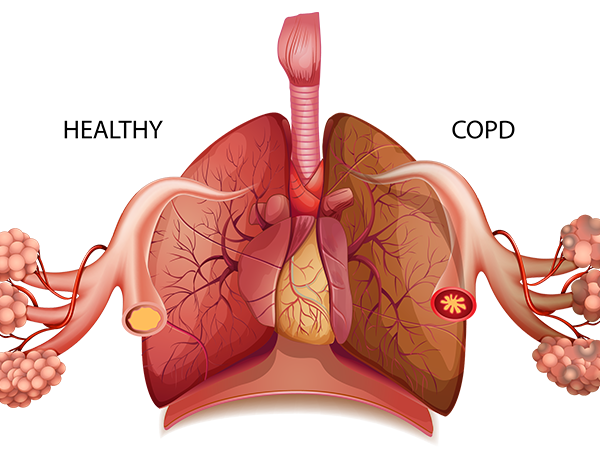
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
COPD such as Emphysema and chronic bronchitis, is a condition that makes it difficult to breathe and gets worse and worse over time. It can cause severe coughing, excess mucus production, wheezing and chest tightness. Main cause is smoking and other major cause is exposure to air pollution. There is no cure for COPD but a healthy diet may help to prevent COPD and help keep it from getting worse. Just one extra serving of fruit each day may translate into a 24 percent lower risk of dying from COPD. However, consumption of meat like bacon, ham, hotdog sausage and salami may increase risk of COPD.
Asthma
Asthma is an inflammatory characterised by recurring attacks of narrowed, swollen airways, causing shortness of breath, wheezing and coughing. It usually emerges during childhood. Foods of animal origin have been associated with increased asthma risk. Thin coating of fluid forms the interface between your respiratory tract lining and the outside air. Using the antioxidants obtained from the fruits and vegetables you eat, this fluid acts as your first line of defense against the free radicals that contribute to asthmatic airway hypersensitivity, contraction and mucus production. If the antioxidants are effective then why not take antioxidant supplements? Studies have repeatedly shown that antioxidant supplements have no beneficial effects on respiratory or allergic diseases, under scoring the importance of eating whole foods rather than trying to take isolated components or extracts in pill form.