Diabetes – Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
About Diabetes
What is Diabetes ? Diabetes mellitus comes from two words : Diabetes (Greek for ‘to pass through’) and mellitus (Latin for ‘honey sweet’). Diabetes mellitus is a nutritional disorder, characterized by an abnormally elevated level of blood glucose and by the excretion of the excess glucose in the urine. This is because either your pancreas gland isn’t making enough insulin (the hormone that keeps your blood sugar in check) or because your body becomes resistant to insulin’s effects. The insulin-deficiency disease is called type 1 diabetes and the insulin resistance disease is called type 2 diabetes.
What is insulin ? Our digestive system breaks down the carbohydrates we eat into a simpler sugar called glucose, which is the primary fuel powering all the cells in our body. To get from the bloodstream into your cells, glucose requires insulin. Every time we eat a meal, insulin is released by our pancreas to help shuttle the glucose into our cells.
Without insulin, your cells can’t accept glucose and as a result, the glucose builds up in your blood. Overtime, extra sugar can damage the blood vessels throughout the body. That’s why diabetes can lead to blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks and stroke.
How to test ? If too much sugar builds up in your blood, it can overwhelm the kidneys and spill into your urine. So before lab techniques, people used to taste urine to check sugar, diabetic urine tastes like honey. Nowadays, the most commonly-used screening tests are the determination of the fasting blood glucose level and the two-hour postprandial, that is after a meal. The normal fasting blood sugar content is 80 to 120 mg per 100 ml of blood and this can go up to a level of 180 mg per 100 ml of blood two hours after meals. Anything above these norms can be termed diabetic levels.

Who gets Diabetes ? Diabetes is a disease known to the medical world since time immemorial. Its incidence is, however, much higher at present than ever in the past. This is especially true in case of more advanced countries of the world due to widespread affluence and more generous food supply.
Diabetes occurs in all age groups, from young infants to the elderly. The greatest incidence occurs in middle or older aged persons. It is estimated that 80 to 85 percent of all individuals with diabetes mellitus are 45 years of age or older.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes
Approx 5 percent of all diabetes cases. In most these cases, the immune system mistakenly destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. So, it can be treated with injections of insulin, a type of hormone replacement therapy, to make up for the lack of production. Exact cause of Type 1 diabetes is unknown but it can be caused due to exposure to environmental triggers as viral infections and/or cow milk may play a role.
Type 2 diabetes
Accounts for 90-95% diabetes cases. In this, pancreas can make insulin but it doesn’t work. The accumulation of fat inside the cells of your muscles and liver interferes with the action of insulin. This fat can come from the fat you eat or the fat you wear (i.e. your body fat). So, prevention, treatment and reversal of type 2 diabetes depends upon diet and lifestyle. Type 2 diabetes is almost always preventable, often treatable and sometimes even reversible through diet and lifestyle changes.
What causes insulin resistance ? When insulin attaches to insulin receptors on a cell, it activates a series of enzymes that escort in the glucose. Now in case of Type 2 diabetes, fat in your bloodstream, either from your own fat stores or from your diet, can buildup inside your muscle cells, where it can create toxic breakdown products and free radicals that block the insulin signaling process.
Symptoms
The world diabetes is derived from the greek word meaning “to siphon; to pass through”, and mellitus comes from the latin word “honey”. Thus two characterstic symptoms, namely, copious urination and glucose in the urine give the name of the disease. The normal volume of urine passed daily is about one and a half litre, but in the diabetic condition it can vary from four to twenty litres. The urine is of pale colour, has an acidic reaction and sweetish odour. The quantity of sugar present in it varies from one-and-a-quarter decigram to two and a half grams the total per day in many cases reaching as much as one kg in 15 litres of urine.
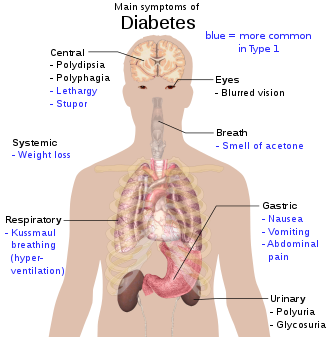
A diabetic feels hungry and thirsty most of the time, does not put on weight, though he eats every now and then, and gets tired easily, both physically and mentally. He looks pale, may suffer from anaemia, constipation, intense itching around the genital organs, palpitations and general weakness. He feels drowsy and has a lower sex urge than a normal person.
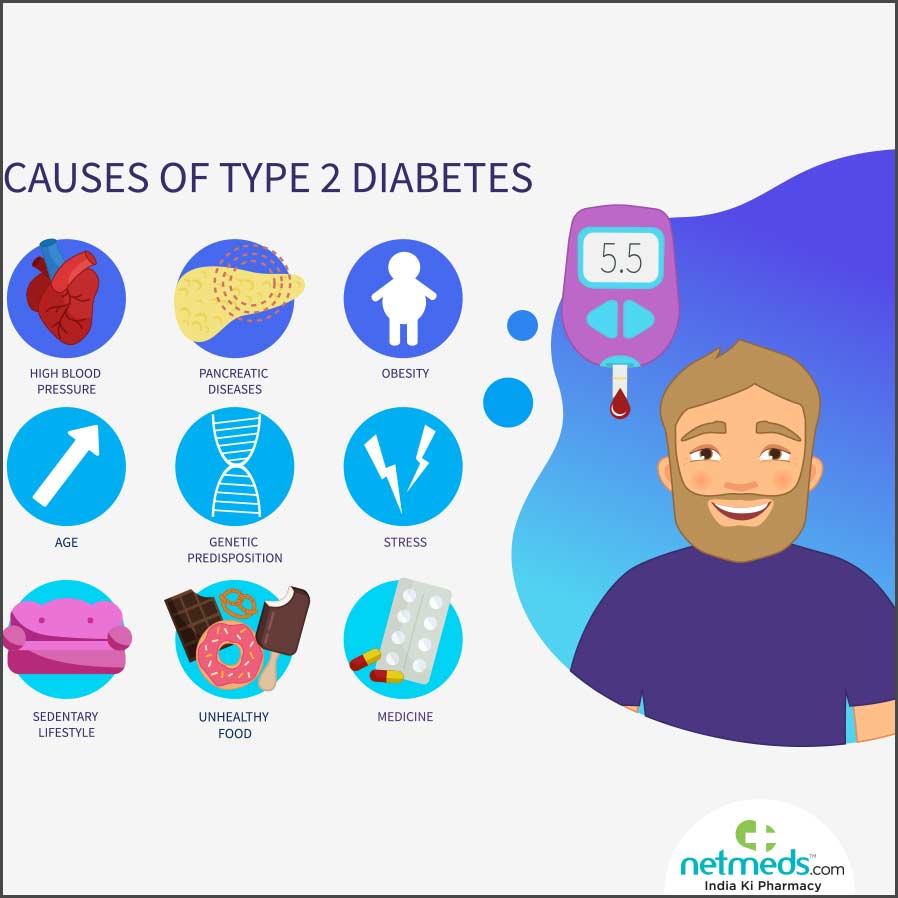
Causes
Diabetes has been described by most biological doctors as a “prosperity” disease, primarily caused by systematic over eating and consequent obesity. Not only the overeating of sugar and refined carbohydrate but also of proteins and fats, which are transformed into sugar if taken in excess, is harmful and may result in diabetes. Too much food taxes the pancreas and eventually paralyses its normal activity.
Obesity and Diabetes
It has been estimated that the incidence of diabetes is four times higher in persons of moderate obesity and 30 times higher in persons of severe obesity.

BMI > 30 (Obese)
BMI = 25 – 29.9 (Overweight)
BMI = 18.5 – 24.9 (Ideal Weight)
In overweight and obese people, the fat cells (with increase in belly doesn’t mean new fat cells but same cells cramming more fat into existing ones) can get so bloated that they actually spill fat back into the bloodstream, causing the same clogging of insulin signaling one would experience from eating a fatty meal. Eliminating meat can reduce risk by 61%. Those who go a step farther and drop eggs and dairy foods too, may drop their diabetes rates 78% compared with people who eat meat on a daily basis. Even among healthy individuals, a high fat diet can impair the body’s ability to handle sugar.
Saturated Fats and Diabetes
Not all fats affect our muscle cells in the same way, e.g., Palmitate, the kind of saturated fat found mostly in meats, dairy, and eggs causes insulin resistance. On the other hand, Oleate, the monounsaturated fat found mostly in nuts, olives and avocados, may actually protect against the detrimental effects of the saturated fat. Saturated fats can wreak all sorts of havoc in muscle cells and may result in the accumulation of more toxic breakdown products (such as ceramide and diacylglycerol) and free radicals and can cause inflammation and even mitochondrial dysfunction. Monosaturated fats, however, are more likely to be detoxified by the body or safely stored away.
Saturated fats may also be toxic to the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. At around age 20, the body stops making new insulin producing beta cells. After that if they are lost, they may be lost for good. The more saturated fat you have in your blood, the higher your risk may be for developing type 2 diabetes.
Other Causes
The genetic component also has effect and who already have a genetic predisposition, a diet with too many calories and rich in saturated fat is considered a cause of type 2 diabetes. It has been rightly said, “Heredity is like a cannon and obesity pulls the trigger”. Diabetics are more likely to suffer from strokes and heart failure.
Grief, worry and anxiety also have a deep influence on the metabolism and may cause sugar to appear in the urine. The disease may be associated with some other grave organic disorders like cancer, tuberculosis and cerebral disease.
Treatment
Any successful method of diabetes treatment should aim at removal of the actual cause of the disease and building up of the whole health-level of the patient. Diet plays a vital role in such a treatment. Fruits, nuts and vegetables, whole meal bread and dairy products form a good diet for the diabetic. These foods are best eaten in as dry a condition as possible to ensure thorough salivation during the first part of the process of digestion.
Plant-Based Diet
Those eating plant-based diets have been found to have better insulin sensitivity, better blood sugar levels, better insulin levels and even significantly improved function of their beta cells – the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin in the first place.
Those who eat plant-based diets may even have an 11 percent higher resting metabolic rate. That means vegetarians could be burning more calories even in their sleep. This could be because vegetarians have a higher gene expression of a fat-burning enzymes called carnitine palmitoyltransferase, which effectively shovels fat into the mitochondrial furnaces in your cells.

Cooked starchy foods
Cooked starchy foods should be avoided as in the process of cooking the cellulose envelops of the starch granules burst and, consequently, the starch is far too easily absorbed in the system. The excess absorbed has to be got rid of by the kidneys and appears as sugar in the urine. With raw starchy foods, however, the saliva and digestive juices in the small intestine regulate the quantities required to be changed into sugar for the body’s needs. The unused and undigested portion of raw starchy foods does not become injurious to the system, as it does not readily ferment.
Fruits and Vegetables
The diabetic should not be afraid to eat fresh fruits and vegetables which contain sugar and starch. Fresh fruits contain sugar fructose, which does not need insulin for its metabolism and is well tolerated by diabetics. Fats and oils should be taken sparingly, for they are apt to lower the tolerance for proteins and starches. Emphasis should be on raw foods as they stimulate and increase insulin production. For protein, homemade cottage cheese, various forms of soured milk and nuts are best. The patient should avoid overeating and take four or five small meals a day rather than three large ones.
Diet Therapy
Celery, cucumbers, string beans, onion and garlic are especially beneficial. String bean pod tea is an excellent natural substitute for insulin and highly beneficial in diabetes. The skin of the pods of green beans are extremely rich in saliva and certain hormone substances which are closely related to insulin. One cup of string bean tea is equal to one unit of insulin. Cucumbers contain a hormone needed by the cells of the pancreas for producing insulin. Onion and garlic have proved beneficial in reducing blood sugar in diabetes.

Bitter Gourd
Recent scientific investigations have established that bitter gourd (karela) is highly beneficial in the treatment of diabetes. It contains an insulin-like principle, known as plant-insulin which has been found effective in lowering the blood and urine sugar levels. It should, therefore, be included liberally in the diet of the diabetic. For better results, the diabetic should take the juice of about four or five fruits every morning on an empty stomach. The seeds of bitter gourd can be added to food in a powdered form. Diabetics can also use bitter gourd in the form of decoction by boiling the pieces in water or in the form of dry powder.
Jambul Fruit
Another effective home remedy is jambul fruit known as jamun in the vernacular. It is regarded in traditional medicine as a specific against diabetes because of its effect on the pancreas. The fruits as such, the seeds and fruit juice are all useful in the treatment of this disease. The seeds contain a glucoside “janboline” which is believed to have the power to check the pathological conversion of starch into sugar in cases of increased production of glucose. They should be dried and powdered. This powder should be taken mixed in milk, curd or water.
The patient should avoid tea, coffee and cocoa because of their adverse influence on the digestive tract. Other foods which should be avoided are white bread, white flour products, sugar, tinned fruits, sweets, chocolates, pastries, pies, puddings, refined cereals and alcoholic drinks.
The most important nutrient in the treatment of diabetes is manganese which is vital in the production of natural insulin. It is found in citrus fruits, in the outer covering of nuts, grains and in the green leaves of edible plants. Other nutrients of special value are zinc, B-complex vitamins and poly-unsaturated fatty acids.
Exercise
Exercise is also an important factor in the treatment of diabetes. Light games, jogging and swimming are recommended. Yogic asanas such as bhujangasana, shalabhasana, dhanurasana, paschimottanasana, sarvangasana, halasana, ardha-matsyendrasana and shavasana, yogic kriyas like jalneti and kujal and pranayamas such as kapalbhati, anuloma-viloma and ujjai are highly beneficial.

Hydrotherapy and colonic irrigations form a very important part of treatment. Bathing in cold water greatly increases the circulation and enhances the capacity of the muscles to utilise sugar.
The diabetic patient should eliminate minor worries from his daily life. He must endeavour to be more easy-going and should not get unduly worked up by the stress and strain of life.
Reversing Diabetes
Blood sugar levels can normalize within a week of eating six hundred calories daily, because fat is pulled out of the muscles, liver and pancreas, allowing them to function normally again. Now, this food restriction can be caused voluntarily (eating less and starve) or involuntarily (undergoing surgery and cut 90% of stomach). But there is one other way : Quality of food. If plant based diet with less calories is adopted diabetes can be reversed.
About one hundred years ago, a single serving of chicken may have contained only sixteen fat calories. Nowadays, one serving of chicken may have more than two hundred calories of fat. The fat content in poultry has ballooned from less than two grams per serving a century ago to up to twenty-three grams today. That’s ten times more fat. Chicken now contains two to three times more calories from fat than from protein.
WHtR versus BMI
BMI only considers weight and height but not distribution of weight. Better way is WHtR (waist to height ratio). Stand up straight and take a deep breath, exhale and let it all hang out. The circumference of your belly (halfway between the top of your hip bones and the bottom of your rib cage) should be half your height – ideally less. If its more than half, time to start eating healthier.