Importance of Dietary Fibre – Sources and Types
Fibre forms the skeletal system of plants. Without it no plant or tree would be able to stand upright. Dietary fibre, the roughage of yesteryears, consists of those parts of the plant foods that cannot be digested by enzymes or other digestive secretions in the alimentary canal.
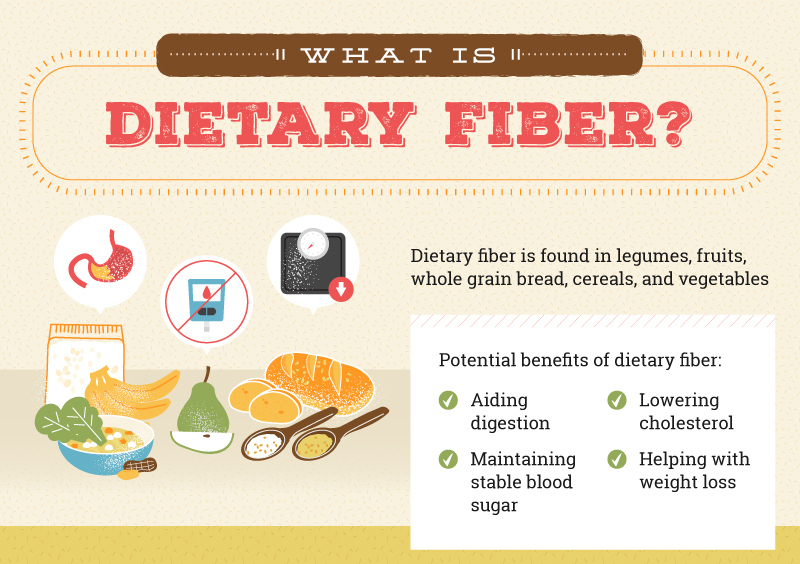
Dietary fibre plays an important role in the maintenance of health and prevention of diseases. There is sufficient evidence to suggest that an artificial depletion of fibre as in case of refined cereals and sugar has over the last 100 years contributed to several degenerative diseases. Recent studies in this area indicate that sufficient intake of fibre-rich diet may help prevent obesity, colon cancer, heart diseases, gallstones, irritable bowel syndrome, diverticulosis and diabetic conditions.
Studies have also established that dietary fibre is a collection of elements with a variety of functions rather than a single substance with single function as was assumed earlier. This new insight into the true nature of fibre has given the lie to old beliefs that bran is synonymous with fibre, that all fibre is fibrous or stringy and that all fibre tastes the same.
Physiological Effects
Fibre in the diet promotes more frequent bowel movements and softer stools having increased weight. The softness of stools is largely due to the presence of emulsified gas which is produced by the bacterial action on the fibre. A high fibre intake results in greater efficiency in the peristaltic movements of the colon. This helps in relieving constipation which is the main cause of several acute and chronic diseases.
Recent studies suggest that increasing the dietary fibre intake may be beneficial for patients with irritated bowel syndrome who have diarrhoea and rapid colonic transit, as well as to those who have constipation and slow transit. This high fibre diet, like bran, thus regulates the condition inside the colon so as to avoid both extremes – constipation and diarrhoea.

Investigations have shown that several potential carcinogens are produced in the faeces. Their production is related to the acidity of the gut content. The greater the acidity in the bowel content, the less is the production of these carcinogens. The breaking down of the fibre by bacteria renders the faeces more acidic. This reduces the amount of possible carcinogenic substances. Fibre also reduces the possibility of formation of harmful toxins in the large intestine by reducing the intestinal transit time of the food contents.
Dietary fibre increases the bacteria in the large intestines which require nitrogen for their growth. This in turn reduces the chances of cancerous changes in cells by reducing the amount of ammonia in the large bowel. Fibre reduces the absorption of cholesterol in the diet. It also slows down the rate of absorption of sugars from the food in the digestive system. Certain types of fibre increases the viscosity of the food content. This increased viscosity indirectly reduces the need for insulin secreted by the pancreas. Thus a fibre-rich diet can help in diabetes mellitus.
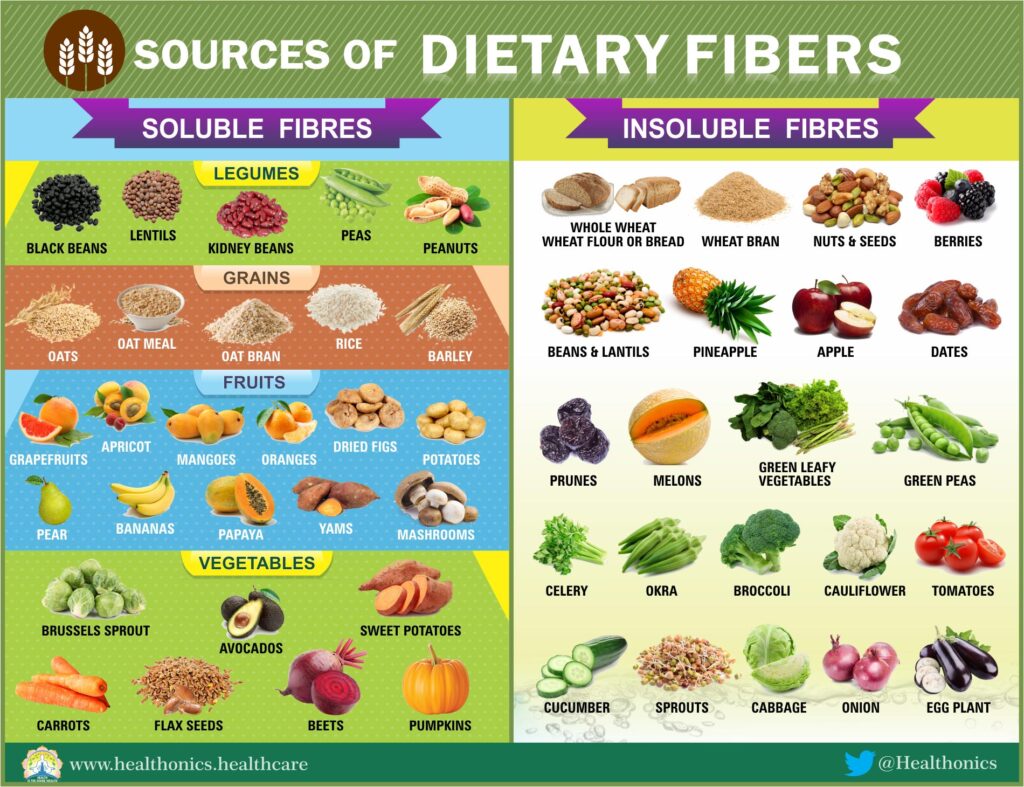
Sources of Fibre
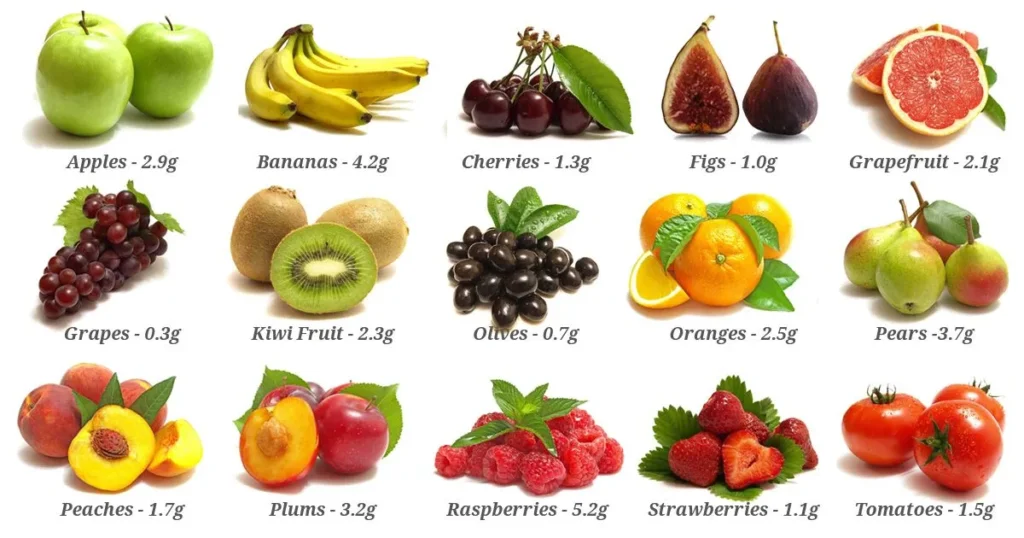
The most significant food sources of fibre are unprocessed wheat bran, whole cereals such as wheat, rice, barley, rye, millets; legumes such as potato, carrots, beet, turnip and sweet potato; fruits like mango and guava and leafy vegetables such as cabbage, lettuce and celery. The percentage of fibre content per 100gms of some foods are : Bran 10.5-13.5, whole grain cereals 1.0-2.0, nuts 2.0-5.0, legumes 1.5-1.7, vegetables 0.5-1.5, fresh fruits 0.5-1.5 and dried fruits 1.0-3.0. The foods which are completely devoid of fibre are meat, fish, eggs, milk, cheese, fats and sugars.

Bran, the outer coverings of grains, is one of the richest sources of dietary fibre. And it contains several types of fibre including cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. Wheat and corn bran are highly beneficial in relieving constipation. Experiments show that oat bran can reduce cholesterol levels substantially. Corn bran is considered more versatile. It relieves constipation and also lowers LDL cholesterol, which is one of more harmful kinds. Besides being rich in fibre, bran has a real food value being rich in lime, iron and vitamins and containing a considerable amount of protein.
Legumes have high fibre content. Much of this fibre is water-soluble, which makes legumes likely agents for lowering cholesterol. Soyabeans, besides this, can also help control glucose levels.
The types of fibre contained in vegetables and fruits contribute greatly towards good health. The vegetables with the biggest fibre ratings include sweet corn, carrots, potatoes, parsnips and peas. And among the high ranking fruits are raspberries, pears, strawberries and guavas.
Types of Fibres
There are six classes of fibre. They are cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin, gums, mucilages and legnin. They differ in physical properties and chemical interactions in the gut, though all except legnin are poly-saceharides. The facts known so far about these forms of fibre as a result of various studies are discussed below :-
Cellulose
It is the most prevalent fibre. It is fibrous and softens the stool. It abounds in fruits, vegetables, bran, whole-meal bread and beans. It is also present in nuts and seeds. It increases the bulk of intestinal waste and eases it quickly through the colon. Investigations indicate that these actions may dilute and flush cancer-causing toxins out of the intestinal tract. They also suggest that cellulose may help level out glucose in the blood and curb weight gain.
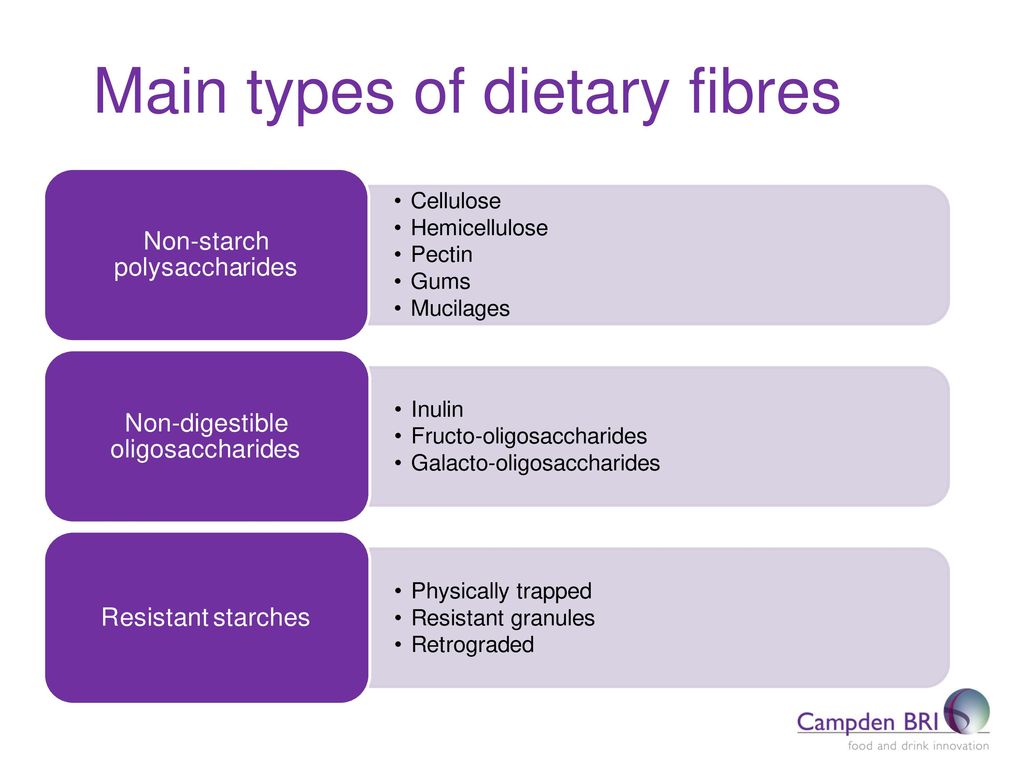
Hemicellulose
It is usually present wherever cellulose is and shares some of its traits. Like cellulose, it helps relieve constipation, waters down carcinogens in the bowel and aids in weight reduction. Both cellulose and hemicellulose undergo some bacterial breakdown in the large intestine and this produces gas.
Pectin
This form of fibre is highly beneficial in reducing serum cholesterol levels. It, however, does not have influence on the stool and does nothing to prevent constipation. Researches are being conducted to ascertain if pectin can help eliminate bile acids through the intestinal tract thereby preventing gallstones and colon cancer. It is found in apples, grapes, berries, citrus fruits, guava, raw papaya and bran.
Gums and Mucilages
They are the sticky fibres found in dried beans, oat bran and oatmeal. Investigations have shown that they are useful in the dietary control of diabetes and cholesterol.
Legnin
The main function of legnin is to escort bile acid and cholesterol out of the intestines. There is some evidence that it may prevent the formation of gallstones. It is contained in cereals, bran, whole meal flour, raspberries, strawberries, cabbage, spinach, parsley and tomatoes.
Increase Fibre content in Diet
The best way to increase fibre content in the diet is to increase the consumption of wholemeal bread, brown rice, peas, beans, lentils, root vegetables and sugar containing fruits such as dates, apples, pears and bananas. The intake of sugar, refined cereals, meat, eggs and dairy products should be reduced. Candies, pastries, cakes which are rich in both sugar and fat, should be taken sparingly. White processed bread should be completely eliminated from the diet.
Requirement
There are divergent views as to the requirement of dietary fibre for good health. There is no recommended daily dietary allowance for it and hardly any data about optimum amounts. Excessive consumption of fibre, especially bran, should however, be avoided. Due to its content of crude fibre, bran is relatively harsh and it may irritate the delicate functioning of the digestive system, especially in the sick and the weak. Excessive use of fibre may also result in loss of valuable minerals like calcium, phosphorus, magnesium and potassium from the body through excretion due to quick passage of food from the intestine.




